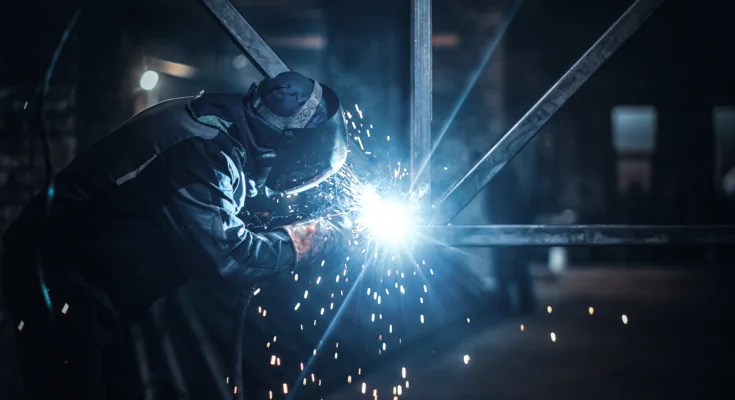
In the industrial world of fabrication and construction, welding has become one of the most important processes, necessary for connecting materials and ensuring strong structures. This article explores the details of welding, their different types, utilization, and advantages.
Welding
Welding is a fabrication method that uses heat and/or pressure to join two or more parts together, resulting in an integrated joint. This method is used with various materials, which range from metals, plastics, and wood.
Benefits of Welding
Welding offers numerous benefits, including
Creating Strong Joints
Welding has joints that are as strong or even stronger than the parent materials, thus maintaining the structure’s integrity.
Repairing Damaged Parts
Welding can restore damaged components prolonging their life and function.
Reducing Material Waste
Through the joining of materials accurately, welding helps in reducing the amount of waste material usage thus promoting sustainability in manufacturing.
Types of Welding
There are several processes within Welding each made for a particular operation and product. Among others, the three most popular types are Arc welding, MIG welding, and TIG welding.
Arc Welding
In Arc welding current, the Arc is created between an electric electrode, and the workpiece. This Arc is giving off considerable heat which melts the base and often a filler material. The benefits of Arc welding include low cost and being easy to apply and the disadvantages are low quality, high spatter contamination and hazards from Arc and slag falling, etc.
Applications of Arc Welding
Arc welding is a popular method that has many applications in the manufacturing sector, specifically in the construction, shipbuilding, and automobile-repair industries, all because of its low price and adaptability.

MIG Welding
MIG welding, known as metal inert gas welding, is a process of welding that uses a thin wire electrode to perform welding operations. When it reaches the welding site electric current is passed through the wire fed into the welding tool and which in turn heats the wire itself. MIG welding can offer productivity and quality, but comes with the cost and demands for shielding gases.
Applications of MIG Welding
The MIG welding is very widely used in many industries which use the manufacturing, fabrication as well as the robotics. MIG welding is highly resourceful and also provides great results for the perfect welds.

TIG Welding
TIG welding, also known as tungsten inert gas welding, is known for its high-quality welds and a wide range of applications. This process uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode and a filler rod to make the weld. TIG welding offers accuracy and strength although it requires qualified welders and the equipment is expensive.
Applications of TIG Welding
Industries like aerospace, nuclear, and medical use TIG welding due to its capability to produce perfect weld in critical parts.

Tips for Choosing the Right Welding Method
Assess Project Requirements
Think on material type, condition of joint affected and quality of usable welding.
Evaluate Cost
Compare the initial capital outlay, purchases of consumable materials and operating costs for each welding process.
Consider Skill Level
Select a welding process that matches with your level of exposure and knowledge.
Review Application Needs
Assess the application environment, location constraints, and production capacity.
Seek Professional Advice
Seek advice and suggestions from skilled welders or seasoned professionals in the field.
Conclusion
Welding becomes a pivotal process in contemporary manufacturing and construction allowing for stable structures and elements. A deep understanding of Arc, MIG and TIG welding enables practitioners to choose the best welding technique for their projects. However, the cost-effectiveness of Arc welding, the efficiency of MIG welding, and the accuracy of TIG welding each represent a unique benefit and application.

FAQs
Q: What safety measures should be taken during welding?
A: Welding professionals must wear helmets and glasses, gloves, and protective outfits; install ventilation operating units to prevent gases and fumes inhalation and maintain welding devices for defects and malfunctions on a regular basis.
Q: Is welding applicable to non-metallic materials?
A: Indeed, welding can be modified for application on materials like plastics and wood; however, it requires specialized tools and procedures.
Q: What determines the welded joint quality?
A: The factors that influence the strength and integrity of a welded joint include the welding method, material preparation, and the surrounding environment.
Q: Is welding a sustainable manufacturing process?
A: Welding may advance in sustainability by minimizing material waste through cost effective repairing and fabrication technologies.
Q: What should I do to become a better welder?
A: Practice welding with the guidance of welders to gain mastery in the field while partake in workshops and training programs to improve your skills and gather information.